|
© I contenuti di questa pagina (escluse le immagini di pubblico dominio) sono di proprietà esclusiva dell'autore Alberto Tucci. Ne è vietata la copia, la riproduzione e l'utilizzo anche parziale in ogni forma. |
| QUESTA SCHEDA È UNICA E ORIGINALE IN INTERNET - aggiornamento 18-01-2026 |
TIMO SERPILLO |
LEGGERE LA SCHEDA IN TUTTE LE SUE SEZIONI PER UNA CORRETTA INFORMAZIONE SULLE PRECAUZIONI D'USO
| COLORI OSSERVATI NEI FIORI |
| ________ LILLÀ |
| ________ ROSA |
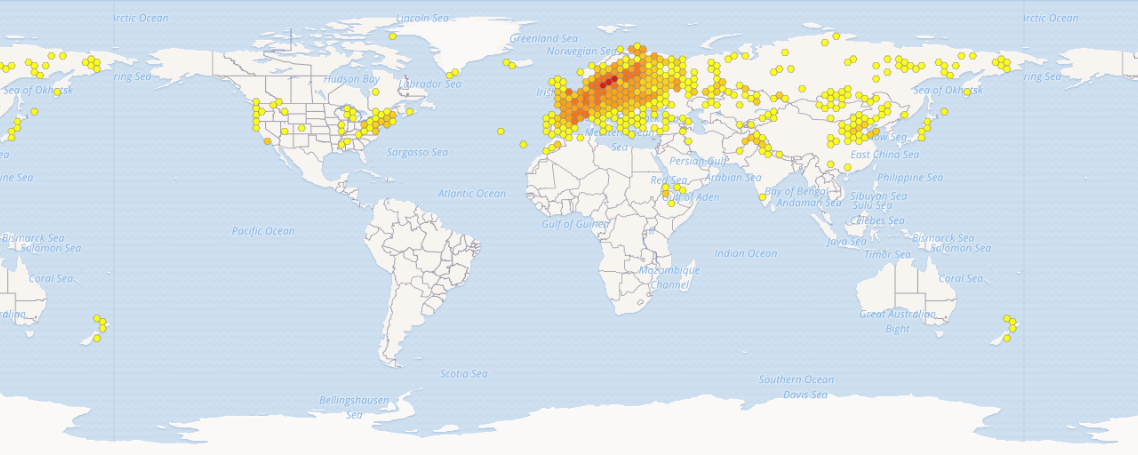
| DISTRIBUZIONE IN BASE ALLE OSSERVAZIONI UMANE |
 |
| TOSSICITÀ: BASSA |
| Motivazione: Nel corretto utilizzo fitoterapico la pianta è generalmente sicura; possono verificarsi lievi disturbi gastrointestinali previsti come parte dell’azione o, raramente, fenomeni irritativi legati all’olio essenziale a dosaggi elevati, senza evidenza di tossicità significativa alle dosi terapeutiche. |
| EFFICACIA: CONFERMATA DA EVIDENZE SCIENTIFICHE |
| Motivazione: Thymus serpyllum L. è documentato per attività antimicrobica, espettorante, antispasmodica e antinfiammatoria grazie ai costituenti fenolici dell’olio essenziale, con conferme da studi in vivo e dati clinici indiretti sull’uso nelle affezioni delle vie respiratorie e gastrointestinali, in continuità con un impiego fitoterapico consolidato. |
| *Note e Bibliografia relativa a proprietà e indicazioni |
| CONTROINDICAZIONI IPERSENSIBILITÀ ACCERTATA AI COMPONENTI (TIMOLO, CARVACROLO), GRAVIDANZA (RISCHIO DI STIMOLAZIONE UTERINA), ALLATTAMENTO (PASSAGGIO DI OLI ESSENZIALI NEL LATTE), BAMBINI SOTTO I 6 ANNI (PER PREPARAZIONI CONCENTRATE), EPILESSIA (POTENZIALE EFFETTO NEUROSTIMOLANTE AD ALTE DOSI), GASTRITE O ULCERA PEPTICA IN FASE ACUTA, INSUFFICIENZA CARDIACA GRAVE |
| AVVERTENZE NON SUPERARE I 4 G/DIE DI DROGA SECCA IN INFUSI, EVITARE L'USO PROLUNGATO (>3 SETTIMANE) SENZA PAUSE, DILUIRE SEMPRE L'OLIO ESSENZIALE (MAX 2-3 GOCCE IN OLIO VETTORE PER USO TOPICO), MONITORARE EVENTUALI REAZIONI ALLERGICHE (RASH CUTANEO, DIFFICOLTÀ RESPIRATORIE), CAUTELA IN PAZIENTI CON IPERTIROIDISMO (POSSIBILE STIMOLAZIONE METABOLICA), EVITARE L'ASSOCIAZIONE CON SEDATIVI O ANSIOLITICI (POTENZIALE INTERAZIONE), PREFERIRE PREPARAZIONI STANDARDIZZATE IN TIMOLO (1-2%) SENTIRE IL PARERE DEL MEDICO PRIMA DELL'ASSUNZIONE DELL'OLIO ESSENZIALE DI SERPILLO |
| * Si tenga presente che talvolta la stessa erba indicata come sinergica o antagonista, potrebbe assumere entrambi i ruoli in funzione della dose utilizzata e/o della forma estrattiva o di trattamento come per es. nel Tè (verde o nero). Consultare sempre un fitoterapeuta per personalizzare le combinazioni in base al quadro clinico individuale. |
BIBLIOGRAFIA, WEBLIOGRAFIA E ARTICOLI SCIENTIFICI SUL WEB (Vedi anche i riferimenti nelle singole sezioni) Prova le ricerche di articoli scientifici su Thymus Serpyllum L. var. |

Hermann Adolph Köhler (1834-1879)

Piperna (Ischia)
Autore: A.Tucci
Autore: A.Tucci
 Altre Foto e Immagini di TIMO SERPILLO
Altre Foto e Immagini di TIMO SERPILLO